what power does the federal government have to regulate the state of california and its residents
The post-obit is a full general background on how state regime works. Please note that each state operates co-ordinate to its own constitution.
- Powers of the Federal Government
- Powers of the States
- State Constitutions
- The Legislature
- Governor
- Revenue
- Education
- State Government Vocabulary
- Bibliography
Powers Reserved for the Federal Authorities
The U.S. government is federal in class. The states and national authorities share powers, which are wholly derived from the Constitution.
From the Constitution, the national government derives
- express powers
- unsaid powers
- inherent powers
Article I, Section 10 of the Constitution of the United States puts limits on the powers of united states of america. States cannot form alliances with foreign governments, declare war, money coin, or impose duties on imports or exports.
Powers Reserved to the States
The Tenth Subpoena declares, "The powers non delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited past information technology to u.s.a., are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people." In other words, states take all powers not granted to the federal regime by the Constitution.
These powers have taken many different forms. States must take responsibleness for areas such as:
- ownership of property
- teaching of inhabitants
- implementation of welfare and other benefits programs and distribution of aid
- protecting people from local threats
- maintaining a justice system
- setting up local governments such as counties and municipalities
- maintaining land highways and setting up the ways of administrating local roads
- regulation of manufacture
- raising funds to support their activities
In many areas, states have a large role but also share administrative responsibility with local and federal governments. Highways, for example, are divided among the 3 different levels. Most states classify roads into primary, secondary, and local levels. This system determines whether the state, county, or local governments, respectively, must pay for and maintain roads. Many states have departments of transportation, which oversee and administrate intrastate transportation. U.S. highways and the interstate system are administered by the national government through the U.S. Section of Transportation.
Mandates
States must also administer mandates set up by the federal authorities. Mostly these mandates contain rules which the states wouldn't normally bear out. For example, the federal regime may require states to reduce air pollution, provide services for the handicapped, or require that public transportation must run into certain safety standards. The federal regime is prohibited past constabulary from setting unfunded mandates. In other words, the federal government must provide funding for programs it mandates.
Grants
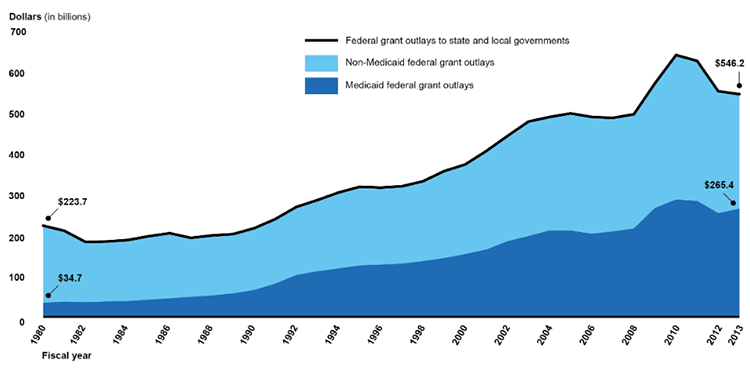
Grants are an important tool used by the federal government to provide program funding to land and local governments. According to the Office of Management and Budget, federal outlays for grants to country and local governments increased from $91 billion in fiscal year 1980 (about $224 billion in 2013 abiding dollars) to about $546 billion in financial twelvemonth 2013. (See figure). Block grants give usa access to large sums of money with few specific limitations. The state must only meet the federal goals and standards. The national authorities can give the states either formula grants or project grants (virtually commonly issued).
Mandates can besides pass from the country to local levels. For case, the state tin can set certain pedagogy standards that the local schoolhouse districts must abide by. Or, states could set rules calling for specific administration of local landfills.
State Constitutions
The Nuts
Each country has its ain constitution which information technology uses equally the footing for laws. All state governments are modeled after the federal government and consist of three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The U.S. Constitution mandates that all states uphold a "republican form" of government, although the iii-co-operative construction is not required.
Therefore, in basic structure land constitutions much resemble the UsaConstitution. They contain a preamble, a bill of rights, articles that describe separation of powers between the executive, legislative and judicial branches, and a framework for setting up local governments.
Length and Specificity
State constitutions also tend to exist significantly more than lengthy than the U.S. Constitution. Country constitutions can contain as many as 174,000 words (Alabama), and have as many as 513 amendments fastened (also Alabama). Much of this length is devoted to problems or areas of interest that are outdated. Oklahoma'due south constitution, for example, contains provisions that draw the correct temperature to examination kerosene and oil. California has sections that describe everything that may exist deemed tax-exempt, including specific organizations and fruit and nut trees under four years of age.
Amendment
All state constitutions provide for a means of amendment. The process is unremarkably initiated when the legislature proposes the amendment past a majority or supermajority vote, after which the people corroborate the subpoena through a majority vote. Amendments can also be proposed by a constitutional convention or, in some states, through an initiative petition.
The Legislature
All states have a bicameral, or two-house legislature, except Nebraska, which has a unicameral, or unmarried, house. Legislative salaries range from nothing (Kentucky and Montana) to $57,500 (New York) per year. In states where in that location is no official salary, legislators are oft paid on a per diem ground (i.e. Rhode Island Legislators earn $5 per twenty-four hour period).
The Upper House
- called the Senate.
- membership tin range from 21 (Delaware) to 67 (Minnesota).
- terms ordinarily concluding four years.
The Lower Firm
- chosen the House of Representatives, General Assembly, or Business firm of Delegates (Virginia),
- membership tin can range from 40 (Alaska and Nevada) to 400 (New Hampshire).
- terms usually last 2 years.
Leadership
Like the national legislature, each house in a land legislature has a presiding officer. The Lieutenant Governor presides over the Senate, but the majority leader assumes virtually of the leadership roles. The house elects a Speaker who serves as its leader. Leaders of each house are responsible for recognizing speakers in debate, referring bills to committee, and presiding over deliberations.
States grant legislatures a multifariousness of functions:
- Enact laws
- Represent the needs of their constituents
- Share budget-making responsibilities with Governor
- Confirm nominations of land officials
- Firm begins impeachment proceedings, Senate conducts the trial if there is an impeachment.
- Casework
- Oversight - review of the executive branch. (east.g., dusk legislation)
Denizen Legislation
Legislators don't wield the only legislative power in state regime. In many states, the people tin perform legislative functions directly. The ways by which these methods can exist implemented vary, but they usually require a certain number of signatures on a petition. After that, the issue is put on the ballot for a general vote.
- Initiative - A manner citizens tin featherbed the legislature and pass laws or amend the country constitution through a directly vote.
- Plebiscite - A way citizens tin can approve of statutes or constitutional changes proposed by the legislature through a directly vote.
- Call up - A way citizens can remove elected officials from office. It is allowed in 14 states and is inappreciably e'er used.
Governor
The Governor is a state's chief executive. A governor can serve either a two or four year term. Thirty-seven states take term limits on the governor.
Roles:
- Appointments
The Governor is chiefly responsible for making appointments to state agencies and offices. These powers include: - The ability to appoint for specific posts in the executive branch.
- The ability to appoint to fill a vacancy caused by the decease or resignation of an elected official
- Main of State
- Chief Executive - draws up budget, also has clemency and military powers
- Veto Power
- Like the U.South. President, a governor has the right to veto bills passed past the legislature.
- Vetoes can exist overridden by a two-thirds or iii-fourths majority in the legislature.
- In many states, the governor has the power of a line-item veto.
- In some states, the governor has the power of an amendatory or conditional veto.
General Governor Information
Other Elected Positions Within the Executive Co-operative
The president and vice-president are the only elected executive positions within the federal government. Country governments, however, ofttimes have other positions executive elected separately from the governor. Some examples include:
- Lieutenant Governor: Succeeds the governor in part and presides over the senate.
- Secretary of State - Takes intendance of public records and documents, also may take many other responsibilities.
- Attorney General - Responsible for representing the state in all court cases.
- Accountant - Makes certain that public money has been spent legally.
- Treasurer - Invests and pays out land funds.
- Superintendent of Public Teaching - Heads country department of teaching.
Revenue
A government'due south revenue system is the entire means by which a authorities acquires funding. States rely on a wide range of revenue sources to fund government. On average, states generate more than 1-third of their revenues from personal income taxes and another ane-tertiary from general sales taxes. The remaining revenues are divide between excise taxes (on gasoline, cigarettes and booze); corporate income and franchise taxes; and taxes on business licenses, utilities, insurance premiums, severance, property and several other sources.That being said, the general character of a state or country and local revenue system is more of import than the nature of any unmarried one of its components.
The relative importance of the major revenue sources for country and local governments changed since 1971. Property taxes declined in importance, and their share was picked upwardly mostly past country private income taxes, charges and miscellaneous revenues. Since state revenue systems have adult gradually and tax policy is used to address multiple objectives, state revenue systems are likely to include inconsistencies.
- Insurance Trust Acquirement relates to the money that the land takes in for administering programs such as retirement, unemployment compensation, and other social insurance systems.
- Services and Fees include items such equally tolls, liquor sales, lottery ticket sales, income from college tuition, hospital charges and utility fees.
- Land Taxes come in many different forms:
Most states have a sales tax. The sales tax is assessed on well-nigh consumer goods in the state and ranges from 4% to 7%. Nigh states besides take a country income tax, like to the one used by the federal authorities. People tin pay upwards to 16% of taxable income in land income taxes. Nigh states have a progressive sales tax. About 37% of state revenue enhancement revenue is obtained through the personal income revenue enhancement. Corporate income tax is also assessed on corporate income, a sum that accounts for 7% of state taxation revenue. States levy taxes on motor fuels such every bit gasoline, diesel, and gasohol. Most of the funds become towards financing roads and transportation within the state. Sin taxes use to alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. These taxes are named as such because they were originally intended to decrease consumption of these "undesirable" goods.Nigh states also take inheritance taxes, where a person pays a percentage of what he or she inherits from a deceased person.
- Lotteries
In 2011, 43 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands have adopted some sort of gambling, near in the form of instant-winner or "cartoon" lotteries. About 1 percentage of state revenue comes from gambling. Lotteries tin can be very profitable for the country. Profits from lotteries have been used towards funding instruction, economic development, and environmental programs. Net income from country lotteries was over $17.75 billion in 2010.
- Debt
Like the Federal authorities, state governments besides have debts. In 2012, total state government debt had reached $757 billion. Debts range from about $114 1000000 in Wyoming to over $120 billion in California.
Educational activity
One of the largest issue areas left to the discretion of usa is educational activity. The United States' public education system is administered mostly on the land and local levels. Elementary and Secondary schools receive funding from all the dissimilar levels of regime: almost 8% from the Federal Government, 50% from the State authorities, and 42% from local governments. State and local governments put more than coin toward education than any other cost. In that location are approximately xv,000 school districts around the country, each governed by its ain school board. The people of the district vote the members of the school board into part. Generally about 15-30% of the local electorate participate in a typical school board election. Some roles of a schoolhouse lath:
- Administer full general district policy
- Make sure the district is in tune with local interests
- Rent or fire the superintendent
The Superintendent is the caput ambassador within a district. His or her responsibilities include:
- Drafting the budget
- Overseeing the principals of schools inside the district
- Full general administration within the district
- Communication with the master state school official (CSSO).
The chief state schoolhouse official is appointed by the governor and, along with other land teaching positions, has many responsibilities:
- distribute state funds
- establish instructor certification requirements
- ascertain length of the school day
- defines nutritional content of school lunches
- mandate sure curricula for schools and ready the school calendar
State Government Vocabulary
amendatory or conditional veto - the power to ship a nib back to the legislature with suggested changes.
casework - taking care of constituents' problems; "errand-running" for particular individuals.
express powers - powers which are directly specified in the Constitution.
federal - a system in which us and national government share responsibilities. When people talk about the federal government, they generally mean the national government, although the term oft refers to the division of powers between the land and national governments.
formula grants - grants given to anyone who meets sure guidelines (grants such every bit those for school lunches, airports or highways).
unsaid powers - powers which are not explicitly stated in the constitution, but which are implied through the "necessary and proper" clause in Commodity I, Section 8.
inherent powers - powers which the national government naturally has to stand for the country in relations with other countries.
line-item veto - the power of a governor to veto particular lines (items) in budget appropriations bills.
mandate - a requirement set by the national government to forcefulness states to perform a particular action.
presiding officer - ane person who oversees the activities of a legislative business firm. A presiding officer can have either a major or pocket-sized leadership office in his or her firm.
project grants - grants given to those who make special requests for assist.
progressive tax - a tax where people with higher incomes pay a college percentage of taxable income in state taxes.
dusk legislation - legislation that has a specific expiration or renewal date. Sunset legislation tin exist used in several situations.
- It tin exist used to persuade legislators who practise non strongly support a detail measure out. When the legislation lasts only a set length of fourth dimension, the "on the fence" legislators are more probable to vote for information technology because of its "temporary" nature.
- Some issues change apace (e.g., technology-related issues), and therefore legislation pertaining to these issues must be updated periodically.
supermajority - a vote which takes a quantity greater than the bulk, ordinarily 2/three or 3/4, to pass.
term limit - a limit on the number of sequent terms an elected official can serve.
unfunded mandate - when the federal government sets regulations for u.s.a. to follow and does not provide the states with funds to carry them out.
Sources:
gao.gov
whitehouse.gov
ncsl.org
pewtrusts.org
galesdevescithhen.blogspot.com
Source: https://votesmart.org/education/states
0 Response to "what power does the federal government have to regulate the state of california and its residents"
Post a Comment